Handling Large Data Sets with Master Loops
- 1 Minute to read
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Handling Large Data Sets with Master Loops
- 1 Minute to read
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Article summary
Did you find this summary helpful?
Thank you for your feedback!
Introduction
When working with large data sets, it can be necessary to loop through the data in manageable chunks. This document outlines a method for looping over more than 1000 objects using a master loop approach in a Logic River.
Determine the Number of Master Loops
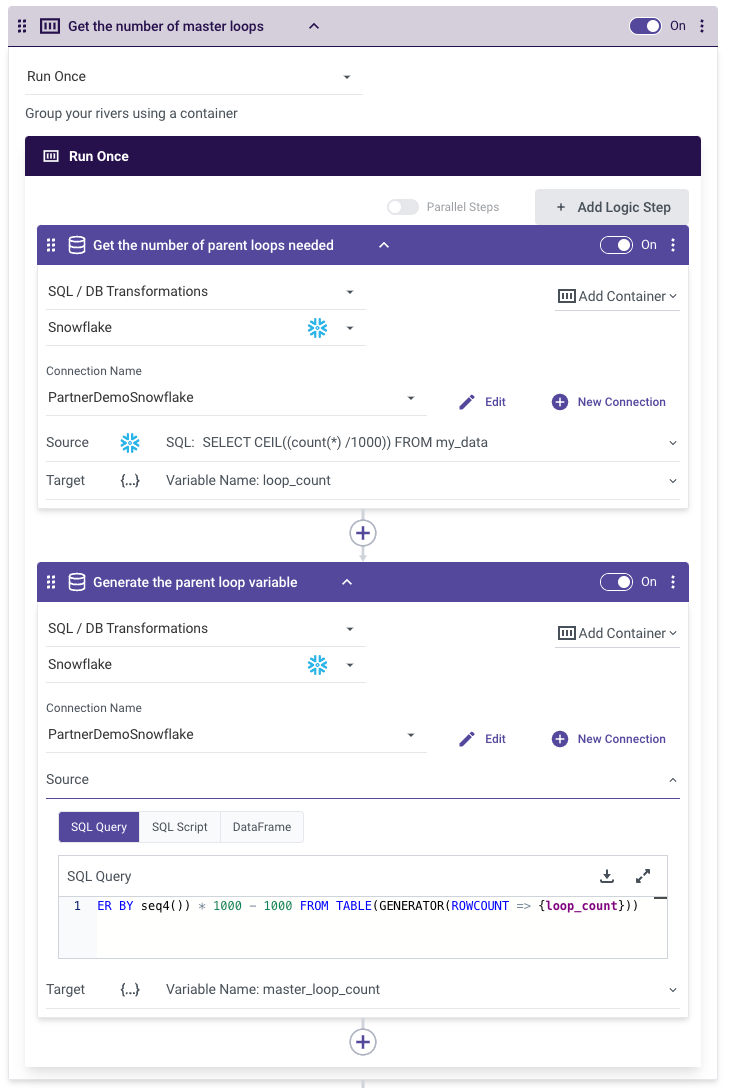
- Get the Number of Parent Loops Needed:
- First, calculate the total number of rows in your data set.
- For example, if my_data has 3335 rows, the following steps will store "4" in the variable loop_count.
Please Note:
my_data is the result of the SELECT ID FROM table statement. These IDs are then passed into the API endpoint to be looped over.
- Generate the Parent Loop Variable:
Generate a list of offsets based on loop_count. This will help parameterize the offset needed to retrieve the right data.
In this example, the list generated would be [0, 1000, 2000, 3000].
Implementing the Loop
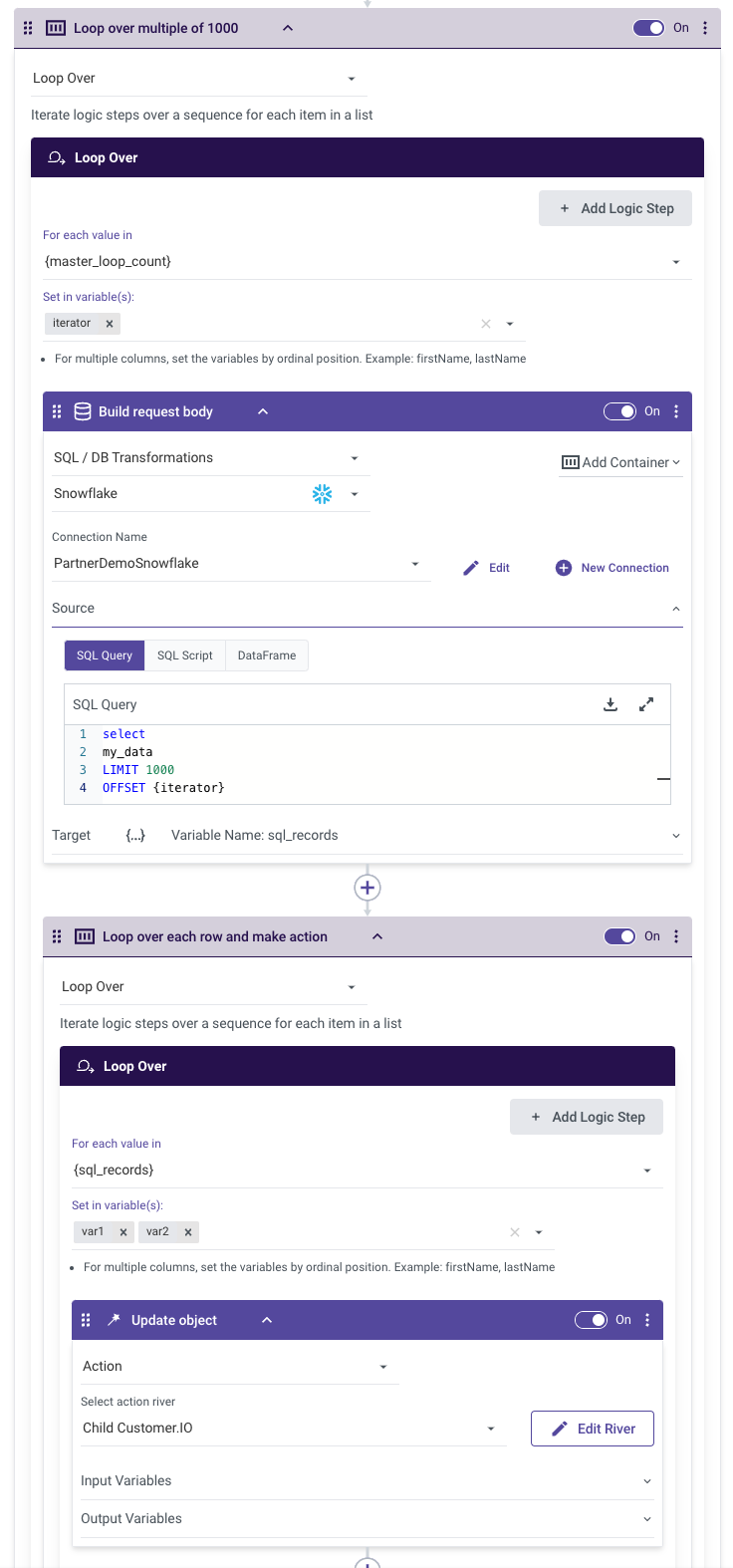
- Master Loop:
- Loop over the list [0, 1000, 2000, 3000].
- Query the Data:
- In each iteration of the master loop, query the data using a limit of 1000 and the appropriate offset. This ensures that each iteration retrieves a subset of the data:
Rows 1 to 1000
Rows 1001 to 2000
Rows 2001 to 3000
Rows 3001 to 3335
- Loop on the Rows and Apply Action:
After querying the data in each iteration, loop through the rows and perform the necessary actions.
Was this article helpful?

