- 5 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
SQL Server CDC Troubleshooting
- 5 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Troubleshooting: When No Data Is Captured In CDC Tables
Check if your table(s) enabled for CDC
In SQL Server, the CDC mechanism creates a job, and a Change Tracking (CT) table for each table separately.
That means, you need to enable any table you want to be capture by the CDC jobs.
Therefore, please refer to our docs on enabling databases and tables in order to make sure the table had been enabled to CDC.
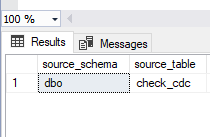
In order to check if the table is enabled for CDC and track changes, please use the next command:
-- The command should return results.
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_help_change_data_capture
GO
And search the table schema and table name under the source_schema and source_name fields.
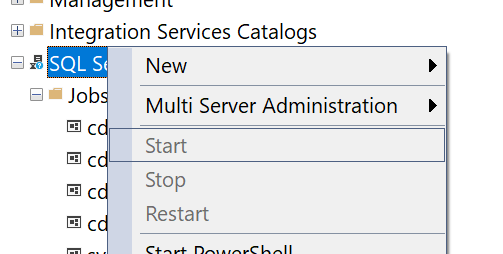
Check if your database has CDC jobs enabled and SQL Server Agent is running
First check that SQL server agent is running by selecting it with right-click:
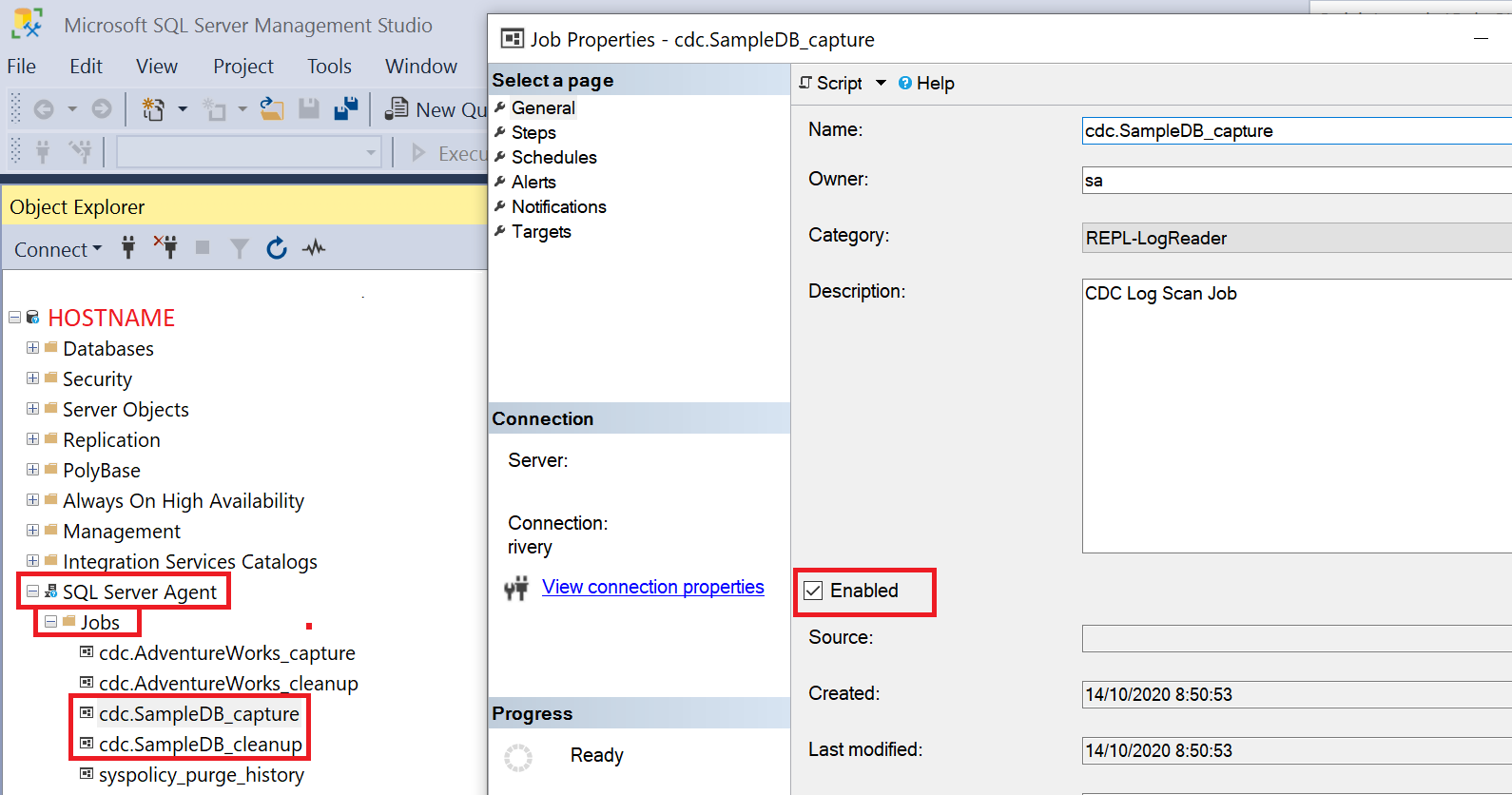
If the database is enabled in CDC and the tables are enabled on CDC and you still can't see new logs coming in, check that the SQL agent for CDC is enabled for capture logs and clean logs. You can do so by downloading Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio, connecting to your data SQL server and underneath:
{HOSTNAME} > SQL Server Agent > Jobs > cdc.{DATABASE}_capture
{HOSTNAME} > SQL Server Agent > Jobs > cdc.{DATABASE}_cleanup
where {HOSTNAME} is your connection's hostname (or the name of the connection you chose), and {DATABASE} is the name of the database you set up for cdc.
you should see enabled jobs.
Please Note:
- A CDC table must have a Primary Key to be tracked by the CDC mechanism in SQL Server, as required by SQL Server.
- Rivery does not support the
@index_nameoption.
Change Tracking Issue Failing After First Run Successful Even After Doing ‘Initiate Migration'
Problem
Error: [RVR-MSSQL-RDBMS-301]: Last synchronization version doesn't exist for this table. Please reinitialize the table data. Please refer to our docs: Page - 'SQL Server Change Tracking', Section - 'Cleanup During River Extraction'.Solution
To address this issue, follow these steps:
1. Check for min_valid_version=0 or missing last_sync_version:
- Verify if the issue is caused by min_valid_version being zero or if last_sync_version is not received.
- If there is no minimum valid version or it’s zero, this error is raised, indicating the need to reinitialize the table. Without the minimum valid version, change tracking data cannot be retrieved.
2. Investigate Cleanup Processes:
- The problem could be due to the cleanup process, which is automated and might occur frequently or rarely depending on various factors.
- Frequent cleanup might remove change tracking data too often, leading to synchronization issues.
3. Review Logs:
- Examine MSSQL server logs for any messages related to change tracking.
- Look for logs about specific issues encountered during the cleanup process or change tracking synchronization.
- Reinitialize the table, run the river, and check the logs after the next run when the error message is raised.
4. Analyze Change Tracking Table Usage:
- Understand the usage of the change tracking tables, as re-initializations happen automatically and could be triggered by multiple factors.
- Determine what caused this issue.
5. Table Update/Delete Frequency:
- Frequent updates or deletions without corresponding inserts might lead to frequent cleanups, causing change tracking to malfunction.
- Check if the table undergoes many updates/deletions.
- Assess if the version column is updated/deleted frequently.
6. Address Concurrency Issues:
- If multiple processes are trying to synchronize with change tracking simultaneously, there could be concurrency issues.
- Ensure the synchronization process is properly coordinated to avoid conflicts, especially if the table is used by multiple rivers.
Start the SQL Server Agent on Azure SQL Server Virtual Machine
In case your SQL Server is running on Azure SQL Server Virtual Machine, there are some cases the SQL Server Agent is needed to be started from the instance itself.
In order to make it, please follow the next steps:
- Go to Azure portal, and search for SQL Server Virtual Machine.
- Click on the right sql server name you want to start the agent on.
- On the SQL Server machine, under the overview, click on the virtual machine name:
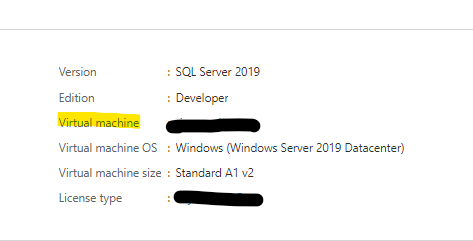
- In the virtual machine that opened, click on Run Command -> RunPowerShellScript:
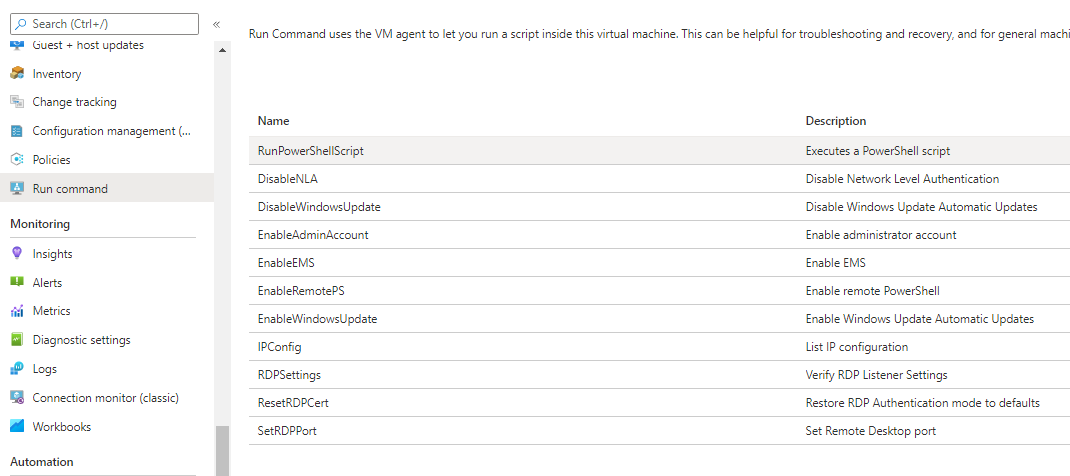
- Run the next script and wait for its end:
> Start-Service SQLSERVERAGENTManaging Source Table Changes
Use Case:
- SQL Server Schema Change migrates DDL (Data Definition Language) but not data.
Overview
When Change Data Capture is enabled for a SQL Server table, event records are persisted to a capture table on the server as changes are made to the table. If you change the structure of the Source table, for example, by adding a new column, the capture table is not dynamically updated.
More information on managing changes to the Source table can be found in Microsoft's documentation.
Update Capture Tables After a Schema Change
Rivery is unable to emit data change events for the table as long as the capture table uses the outdated schema. To allow Rivery to resume processing change events, you must refresh the capture table by performing the following steps:
1. Disable your SQL Server's CDC River. Set the toggle to false and then click 'Disable Stream and Schedule'.
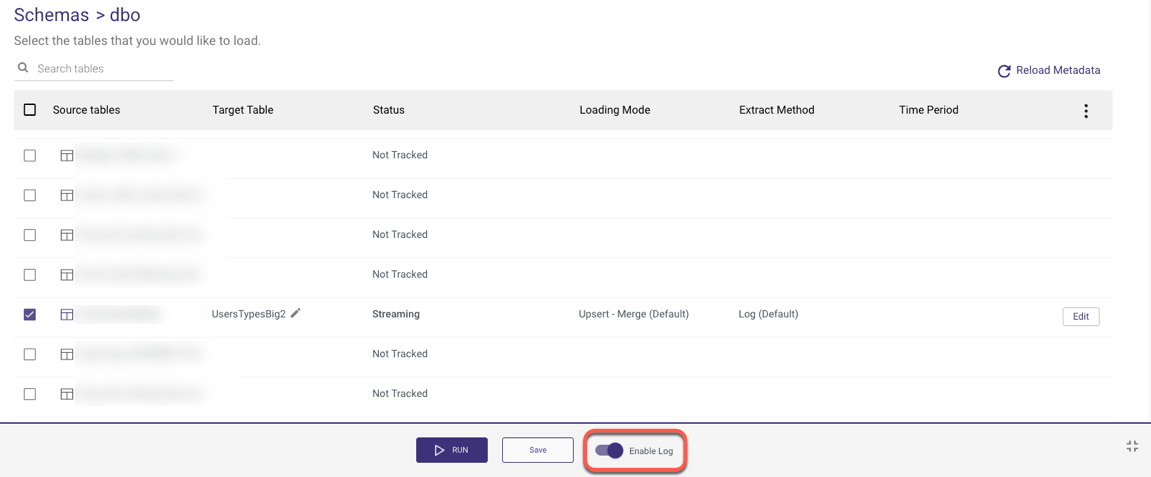
2. Add a new column in your source database.
3. Create a new CDC instance for the table containing the new column by obtaining the name of the table's capture instance containing the new column:
Note: '<schema>' and '<table>' are the schema and table that contain the new column.
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_help_change_data_capture @source_schema = '<schema>', @source_name = '<table>';
4. Disable the current instance of CDC:
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_disable_table @source_schema = [<schema>], @source_name = [<table>], @capture_instance = [<capture_instance>];
Please Note:
- '<schema>' and '<table>' are the schema and table that contain the new column, and [<capture instance>] is the name of the capture instance for the table containing the added column.
- During this process, no new data should be inserted, and writing into the table should be stopped; the old data will be saved by Rivery.
5. Create a new CDC instance:
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_table @source_schema = [<schema>], @source_name = [<table>], @role_name = [<username>];
Note: '<schema>' and '<table>' are the schema and table that contain the new column, and [<username>] is the Rivery username.
6. Remove the previous CDC instance. Make sure that the table has only one CDC instance.
7. Configure a new SQL Server CDC River and ensure that the Source table is visible in the schema.
Current Stream Position in Your Database
To confirm the Stream position, run the following command on the server:
-- For the latest LSN in the transaction log
SELECT TOP 1
[Current LSN]
FROM
sys.fn_dblog(NULL, NULL)
ORDER BY
[Current LSN] DESC;
